Java List 完全指南
"List 是数据序列的艺术" —— 从动态数组到双向链表,掌握List就掌握了序列操作的核心
🎯 为什么需要 List?
在软件开发中,我们经常需要处理有序的数据集合。传统的数组虽然简单,但在动态数据管理方面存在局限:
// ❌ 传统数组的限制
String[] array = new String[5]; // 固定容量
array[0] = "A";
array[1] = "B";
// 想要添加第6个元素?需要创建新数组并复制所有元素!
// ✅ List 的优势
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("A"); // 动态扩容
list.add("B"); // 自动管理容量
list.add("C"); // 无需关心容量问题
List 的核心价值
- 🔄 动态扩容:无需预知数据量,自动管理内存
- 📊 有序性保证:严格保持插入顺序,支持位置操作
- ⚡ 丰富API:提供增删改查等完整操作
- 🧰 泛型支持:编译时类型安全,避免运行时错误
- 🔧 多种实现:根据场景选择最优的数据结构
List 是 Java 集合框架的核心接口,用于表示有序的元素序列。想象一列火车:每个车厢都有位置,可以重复,支持按位置查找和操作。
🎯 快速索引
- 基础概念 - 5分钟理解List核心特性
- 实现类对比 - 选择最适合的List实现
- ArrayList深度解析 - 面试必问的底层原理
- LinkedList详解 - 链表操作的精髓
- 实战应用 - 真实项目中的使用模式
- 性能优化 - 提升应用性能的技巧
- 高频面试题 - 拿下offer的关键点
🌍 什么是 List 集合?
List 核心特性
List 是 Java 集合框架的核心接口,继承自 Collection,表示有序的、可重复的元素序列:
| 特性 | 说明 | 实际场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 📊 有序性 | 严格保持插入顺序 | 用户消息记录、操作日志 |
| 🔄 可重复 | 相同元素可多次出现 | 购物车、标签系统 |
| ⚡ 索引访问 | O(1)时间复杂度访问 | 分页查询、位置操作 |
| 📈 动态扩容 | 自动管理容量增长 | 动态数据收集 |
| 🧰 null支持 | 可存储null元素 | 可选配置项处理 |
List 接口层次结构
RandomAccess 接口的重要性
RandomAccess 是一个标记接口,用于标识 List 实现是否支持高效的随机访问:
// 检查是否支持随机访问
public static void optimalTraversal(List<?> list) {
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) {
// ✅ ArrayList - 使用索引遍历
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Object element = list.get(i);
processElement(element);
}
} else {
// ✅ LinkedList - 使用迭代器遍历
Iterator<?> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object element = iterator.next();
processElement(element);
}
}
}
| 实现类 | 是否实现 RandomAccess | 推荐遍历方式 | 性能特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
ArrayList | ✅ 是 | 索引遍历 for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) | O(1) 随机访问 |
LinkedList | ❌ 否 | 迭代器遍历 | O(n) 随机访问,O(1) 顺序访问 |
Vector | ✅ 是 | 索引遍历 | 线程安全,但有同步开销 |
CopyOnWriteArrayList | ✅ 是 | 索引遍历 | 读操作无锁,写操作复制数组 |
性能对比矩阵
public class ListPerformanceMatrix {
// 基准测试数据
private static final int ELEMENTS = 100_000;
private static final int OPERATIONS = 10_000;
// 测试方法对比
public static void performanceComparison() {
System.out.println("=== List 性能对比矩阵 ===");
System.out.println("测试元素数量: " + ELEMENTS);
System.out.println("操作次数: " + OPERATIONS);
System.out.println();
// 不同场景下的性能对比
List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(ELEMENTS);
List<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> vector = new Vector<>(ELEMENTS);
List<String> cowList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// 填充测试数据
for (int i = 0; i < ELEMENTS; i++) {
String item = "item_" + i;
arrayList.add(item);
linkedList.add(item);
vector.add(item);
cowList.add(item);
}
// 性能测试结果表格
System.out.println("| 操作类型 | ArrayList | LinkedList | Vector | CopyOnWriteArrayList |");
System.out.println("|----------|----------|------------|--------|---------------------|");
System.out.println("| 尾部添加 | O(1)* | O(1) | O(1)* | O(n) |");
System.out.println("| 头部添加 | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |");
System.out.println("| 中间插入 | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |");
System.out.println("| 按索引访问 | O(1) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |");
System.out.println("| 按值查找 | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |");
System.out.println("| 删除元素 | O(n) | O(1)* | O(n) | O(n) |");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("* 表示平均时间复杂度,ArrayList可能触发扩容");
System.out.println("* LinkedList删除时,如果已有节点引用则为O(1),否则需要O(n)查找");
}
}
List vs Array 对比
| 维度 | Array | List |
|---|---|---|
| 容量管理 | 固定长度 | 动态扩容 |
| 操作便利性 | 基础操作 | 丰富的方法API |
| 类型安全 | 基础类型+Object | 泛型保证类型安全 |
| 性能特征 | 访问极快 | ArrayList访问快,LinkedList增删快 |
| 内存布局 | 连续内存 | 数组连续,链表分散 |
与数组的区别
💡 List 应用场景矩阵
| 业务场景 | 推荐实现 | 性能特点 | 代码示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 用户操作历史 | ArrayList | 快速按时间查看 | List<UserAction> actions = new ArrayList<>(); |
| 任务队列 | LinkedList | 频繁头尾操作 | Queue<Task> taskQueue = new LinkedList<>(); |
| 配置项管理 | ArrayList | 读多写少 | List<ConfigItem> configs = new ArrayList<>(); |
| 实时数据流 | CopyOnWriteArrayList | 读多写少,并发安全 | List<Event> events = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); |
| 浏览器历史 | LinkedList | 支持前进后退 | Deque<HistoryEntry> history = new LinkedList<>(); |
| 分页数据缓存 | ArrayList | 随机访问分页数据 | List<PageData> cache = new ArrayList<>(100); |
🧠 ArrayList 深度解析
核心参数配置
public class ArrayList<E> {
// 默认初始容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
// 空数组实例(用于指定容量为0的构造)
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
// 默认空数组实例(用于无参构造)
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
// 存储元素的数组缓冲区
transient Object[] elementData;
// ArrayList中元素的数量
private int size;
// 数组最大容量限制
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
}
构造函数对比
| 构造方式 | 初始容量 | 适用场景 | 性能影响 |
|---|---|---|---|
new ArrayList<>() | 0(首次add时为10) | 不确定元素数量 | 可能触发扩容 |
new ArrayList<>(int capacity) | 指定容量 | 预估元素数量 | 避免扩容损耗 |
new ArrayList<>(Collection<? extends E> c) | 集合大小 | 从其他集合转换 | 直接复制,无扩容 |
扩容机制详解
扩容源码分析
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 1.5倍扩容
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 复制到新数组,O(n)时间复杂度
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // 溢出
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
容量优化实战
public class ArrayListOptimization {
// ❌ 错误:频繁扩容
public List<String> badPractice() {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 默认容量10
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
list.add("item" + i); // 会触发多次扩容:10→15→22→33→49→73→...
}
return list;
}
// ✅ 正确:预估容量
public List<String> goodPractice() {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(10000); // 预设容量
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
list.add("item" + i); // 无需扩容,直接插入
}
return list;
}
// 🔧 实用:容量计算工具
public static int calculateOptimalCapacity(int expectedSize, float loadFactor) {
return (int) (expectedSize / loadFactor) + 1;
}
// 使用示例
public List<String> optimalList(int expectedElements) {
int capacity = calculateOptimalCapacity(expectedElements, 0.75f);
return new ArrayList<>(capacity);
}
}
🔗 LinkedList 双向链表的艺术
节点结构分析
private static class Node<E> {
E item; // 节点数据
Node<E> next; // 下一个节点
Node<E> prev; // 前一个节点
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
内存布局可视化
LinkedList 内存结构:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ first │ ┌─────────────┐ │ last │
│ ───────→ │ │ Node │ ←──────── │
│ │ │─────────────│ │
│ │ │ prev│item│next │ │
│ │ │─────│─────│─────│ │
│ │ │ │ │A │ │ │ │
│ │ │─────│─────│─────│ │
│ │ │ ↓ │ ↓ │
│ │ │ ┌─────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ │ Node │ │ │
│ │ │ │─────────────│ │ │
│ │ │ │ prev│item│next │ │ │
│ │ │ └─────│─────│─────┘ │ │
│ │ │ ↓ │ │ │
│ │ │ ... │ null │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
核心操作时间复杂度
| 操作 | ArrayList | LinkedList | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| get(index) | O(1) | O(n) | 随机访问性能差异巨大 |
| add(E) | O(1)* | O(1) | ArrayList偶尔需要扩容 |
| add(index, E) | O(n) | O(n) | LinkedList需要先查找位置 |
| addFirst(E) | O(n) | O(1) | LinkedList头插入优势 |
| addLast(E) | O(1)* | O(1) | 两者尾部插入都很快 |
| remove(index) | O(n) | O(n) | ArrayList需要移动元素 |
| removeFirst() | O(n) | O(1) | LinkedList头删除优势 |
| removeLast() | O(1) | O(1) | ArrayList尾删除优势 |
双向链表核心方法
public class LinkedList<E> {
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
transient int size = 0;
// 头部添加 - O(1)
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 尾部添加 - O(1)
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 指定位置添加 - O(n)
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
// 查找节点 - 优化的双向查找
Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < (size >> 1)) { // 从前半部分查找
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else { // 从后半部分查找
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
}
⚡ 性能优化指南
1. 初始容量优化
// 容量预估公式
public class CapacityOptimizer {
// 根据预期元素数量计算最优初始容量
public static int calculateOptimalCapacity(int expectedSize) {
// ArrayList扩容因子为1.5,考虑一定的余量
return (int) (expectedSize * 1.3) + 1;
}
// 动态调整容量的工具方法
public static <T> List<T> createOptimizedList(
Collection<T> source, float growthFactor) {
int capacity = (int) (source.size() * growthFactor);
return new ArrayList<>(capacity);
}
}
2. 遍历性能对比
public class TraversalPerformance {
// ArrayList - 最优遍历方式
public void traverseArrayList(List<String> list) {
// ✅ 随机访问,性能最优 - O(n)
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String item = list.get(i);
processItem(item);
}
// ✅ 增强for循环,编译器优化 - O(n)
for (String item : list) {
processItem(item);
}
// ❌ 避免在ArrayList中使用迭代器 - 有额外开销
for (Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) {
String item = it.next();
processItem(item);
}
}
// LinkedList - 最优遍历方式
public void traverseLinkedList(List<String> list) {
// ✅ 迭代器遍历,性能最优 - O(n)
for (String item : list) {
processItem(item);
}
// ✅ 显式迭代器 - O(n)
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String item = it.next();
processItem(item);
}
// ❌ 避免在LinkedList中使用随机访问 - O(n²)
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String item = list.get(i); // 每次get都是O(n)
processItem(item);
}
}
}
3. 批量操作优化
public class BatchOperationOptimization {
// ❌ 低效:逐个添加
public void inefficientAdd(List<String> source, List<String> target) {
for (String item : source) {
target.add(item); // 可能多次触发扩容
}
}
// ✅ 高效:批量添加
public void efficientAdd(List<String> source, List<String> target) {
target.addAll(source); // 一次性添加,只扩容一次
}
// 批量删除优化
public void batchRemove(List<String> list, Set<String> toRemove) {
// ✅ 使用removeAll - 优化版本
list.removeAll(toRemove);
// ✅ 使用迭代器安全删除
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
if (toRemove.contains(iterator.next())) {
iterator.remove();
}
}
// ✅ Java 8+ 使用removeIf
list.removeIf(toRemove::contains);
}
// 大数据量分批处理
public void processInBatches(List<String> largeList, int batchSize) {
for (int i = 0; i < largeList.size(); i += batchSize) {
int end = Math.min(i + batchSize, largeList.size());
List<String> batch = largeList.subList(i, end);
processBatch(batch);
}
}
}
4. 内存优化技巧
public class MemoryOptimization {
// 1. 使用trimToSize减少内存占用
public void optimizeMemoryUsage(List<String> list) {
// 当List不再增长时,可以缩减容量
if (list instanceof ArrayList) {
((ArrayList<String>) list).trimToSize();
}
}
// 2. 原始类型集合减少装箱开销
public void avoidBoxingOverhead() {
// ❌ 自动装箱,有GC压力
List<Integer> boxedList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
boxedList.add(i); // 每次都创建Integer对象
}
// ✅ 使用原始类型集合
// 需要引入第三方库如 fastutil 或 Eclipse Collections
// IntList intList = new IntArrayList();
// for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
// intList.add(i);
// }
}
// 3. 及时清理大List
public void clearLargeLists() {
List<LargeObject> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 使用完后及时清理
list.clear(); // 清理引用,帮助GC
}
}
🎯 List 实战应用与最佳实践
1. 高性能批量操作工具类
public class ListBatchUtils {
/**
* 分批处理大数据集,避免内存溢出
*/
public static <T> void processInBatches(List<T> items, int batchSize,
Consumer<List<T>> batchProcessor) {
if (items == null || items.isEmpty() || batchSize <= 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < items.size(); i += batchSize) {
int end = Math.min(i + batchSize, items.size());
List<T> batch = items.subList(i, end);
batchProcessor.accept(new ArrayList<>(batch));
}
}
/**
* 并行分批处理,提升处理速度
*/
public static <T> CompletableFuture<Void> processInParallelBatches(
List<T> items, int batchSize, Consumer<List<T>> batchProcessor) {
return CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
List<CompletableFuture<Void>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < items.size(); i += batchSize) {
int end = Math.min(i + batchSize, items.size());
List<T> batch = items.subList(i, end);
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
batchProcessor.accept(new ArrayList<>(batch));
});
futures.add(future);
}
// 等待所有批次处理完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])).join();
});
}
/**
* 批量数据库插入
*/
public static <T> void batchInsertToDatabase(
List<T> items, int batchSize, DatabaseRepository<T> repository) {
processInBatches(items, batchSize, batch -> {
repository.batchInsert(batch);
log.info("批量插入了 {} 条记录", batch.size());
});
}
// 使用示例
public static void exampleUsage() {
List<User> largeUserList = fetchUsersFromCache(); // 假设有10万条数据
// 串行处理
ListBatchUtils.processInBatches(largeUserList, 1000, batch -> {
// 处理每1000个用户
processBatch(batch);
});
// 并行处理
CompletableFuture<Void> parallelProcessing =
ListBatchUtils.processInParallelBatches(largeUserList, 1000, batch -> {
processBatch(batch);
});
parallelProcessing.join();
}
}
2. 分页查询实现
public class PaginationHelper {
public static <T> List<T> getPage(List<T> list, int page, int pageSize) {
if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
int fromIndex = (page - 1) * pageSize;
int toIndex = Math.min(fromIndex + pageSize, list.size());
if (fromIndex >= list.size()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return new ArrayList<>(list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex));
}
public static <T> PageResult<T> paginate(List<T> list, int page, int pageSize) {
int totalItems = list.size();
int totalPages = (int) Math.ceil((double) totalItems / pageSize);
List<T> items = getPage(list, page, pageSize);
return new PageResult<>(
items, page, pageSize, totalItems, totalPages
);
}
/**
* 内存友好的大List分页迭代器
*/
public static class PageableIterator<T> implements Iterator<List<T>>, AutoCloseable {
private final List<T> sourceList;
private final int pageSize;
private int currentPage;
private final int totalPages;
public PageableIterator(List<T> sourceList, int pageSize) {
this.sourceList = sourceList;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.totalPages = (int) Math.ceil((double) sourceList.size() / pageSize);
this.currentPage = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return currentPage < totalPages;
}
@Override
public List<T> next() {
if (!hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return getPage(sourceList, ++currentPage, pageSize);
}
public PageInfo getPageInfo() {
return new PageInfo(currentPage, pageSize, totalPages, sourceList.size());
}
@Override
public void close() {
// 清理资源,如果有的话
}
}
public static class PageResult<T> {
private final List<T> items;
private final int currentPage;
private final int pageSize;
private final int totalItems;
private final int totalPages;
private final boolean hasNext;
private final boolean hasPrevious;
public PageResult(List<T> items, int currentPage, int pageSize,
int totalItems, int totalPages) {
this.items = items;
this.currentPage = currentPage;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.totalItems = totalItems;
this.totalPages = totalPages;
this.hasNext = currentPage < totalPages;
this.hasPrevious = currentPage > 1;
}
// getters...
}
public static class PageInfo {
private final int currentPage;
private final int pageSize;
private final int totalPages;
private final int totalItems;
// constructor and getters...
}
}
3. List 工具类 - 生产级实现
public class ListUtils {
/**
* 安全的空List创建
*/
public static <T> List<T> emptyIfNull(List<T> list) {
return list == null ? Collections.emptyList() : list;
}
/**
* List分区 - 保持原始顺序
*/
public static <T> List<List<T>> partition(List<T> list, int size) {
if (list == null || list.isEmpty() || size <= 0) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<List<T>> partitions = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i += size) {
partitions.add(new ArrayList<>(
list.subList(i, Math.min(i + size, list.size()))
));
}
return partitions;
}
/**
* List去重 - 保持顺序
*/
public static <T> List<T> distinct(List<T> list) {
if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Set<T> seen = new LinkedHashSet<>();
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (T item : list) {
if (seen.add(item)) {
result.add(item);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* List交集 - 保持list1的顺序
*/
public static <T> List<T> intersection(List<T> list1, List<T> list2) {
if (list1 == null || list2 == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Set<T> set2 = new HashSet<>(list2);
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (T item : list1) {
if (set2.contains(item)) {
result.add(item);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* List差集 (list1 - list2) - 保持list1的顺序
*/
public static <T> List<T> difference(List<T> list1, List<T> list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
if (list2 == null) {
return new ArrayList<>(list1);
}
Set<T> set2 = new HashSet<>(list2);
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (T item : list1) {
if (!set2.contains(item)) {
result.add(item);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 滚动窗口 - 用于时间序列分析
*/
public static <T> List<List<T>> slidingWindow(List<T> list, int windowSize) {
if (list == null || list.isEmpty() || windowSize <= 0 || list.size() < windowSize) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<List<T>> windows = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= list.size() - windowSize; i++) {
windows.add(new ArrayList<>(list.subList(i, i + windowSize)));
}
return windows;
}
/**
* 智能的List容量预估
*/
public static <T> List<T> createOptimizedList(int expectedSize, float growthFactor) {
int capacity = (int) (expectedSize * growthFactor) + 1;
return new ArrayList<>(capacity);
}
/**
* 从其他集合创建优化容量的List
*/
public static <T> List<T> createFromCollection(Collection<T> collection, float growthFactor) {
if (collection == null || collection.isEmpty()) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
int capacity = (int) (collection.size() * growthFactor) + 1;
return new ArrayList<>(capacity);
}
/**
* 安全的List转数组
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] toArray(List<T> list, Class<T> componentType) {
if (list == null) {
return (T[]) Array.newInstance(componentType, 0);
}
return list.toArray((T[]) Array.newInstance(componentType, list.size()));
}
/**
* List分组
*/
public static <T, K> Map<K, List<T>> groupBy(List<T> list, Function<T, K> keyExtractor) {
if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
return list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(keyExtractor));
}
}
4. 实际业务场景应用
public class ListBusinessApplications {
/**
* 用户行为轨迹分析
*/
public static class UserBehaviorAnalyzer {
private final List<UserAction> actions;
public UserBehaviorAnalyzer(List<UserAction> actions) {
this.actions = new ArrayList<>(actions);
}
/**
* 查找用户连续操作模式
*/
public List<List<UserAction>> findConsecutiveActions(String actionType, int minCount) {
List<List<UserAction>> patterns = new ArrayList<>();
List<UserAction> currentPattern = new ArrayList<>();
for (UserAction action : actions) {
if (action.getType().equals(actionType)) {
currentPattern.add(action);
} else {
if (currentPattern.size() >= minCount) {
patterns.add(new ArrayList<>(currentPattern));
}
currentPattern.clear();
}
}
// 检查最后一个模式
if (currentPattern.size() >= minCount) {
patterns.add(currentPattern);
}
return patterns;
}
/**
* 时间窗口内的操作统计
*/
public Map<String, Integer> getActionStatsInTimeWindow(long startTime, long endTime) {
return actions.stream()
.filter(action -> action.getTimestamp() >= startTime && action.getTimestamp() <= endTime)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
UserAction::getType,
Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.counting(), Math::toIntExact)
));
}
}
/**
* 购物车业务逻辑
*/
public static class ShoppingCartService {
private final Map<String, List<CartItem>> userCarts = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void addItem(String userId, CartItem item) {
List<CartItem> cart = userCarts.computeIfAbsent(userId, k -> new ArrayList<>());
// 查找是否已存在相同商品
Optional<CartItem> existingItem = cart.stream()
.filter(cartItem -> cartItem.getProductId().equals(item.getProductId()))
.findFirst();
if (existingItem.isPresent()) {
// 更新数量
existingItem.get().setQuantity(existingItem.get().getQuantity() + item.getQuantity());
} else {
// 添加新商品
cart.add(item);
}
}
public void removeItem(String userId, String productId) {
List<CartItem> cart = userCarts.get(userId);
if (cart != null) {
cart.removeIf(item -> item.getProductId().equals(productId));
}
}
public BigDecimal calculateTotal(String userId) {
List<CartItem> cart = userCarts.get(userId);
if (cart == null || cart.isEmpty()) {
return BigDecimal.ZERO;
}
return cart.stream()
.map(item -> item.getPrice().multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(item.getQuantity())))
.reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);
}
/**
* 批量添加商品到购物车
*/
public void batchAddItems(String userId, List<CartItem> items) {
if (items == null || items.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
List<CartItem> cart = userCarts.computeIfAbsent(userId, k -> new ArrayList<>(items.size()));
for (CartItem item : items) {
addItem(userId, item);
}
}
}
/**
* 推荐系统中的相似度计算
*/
public static class RecommendationEngine {
/**
* 计算两个用户购买历史的相似度(Jaccard相似系数)
*/
public double calculateUserSimilarity(List<String> user1Items, List<String> user2Items) {
if (user1Items == null || user2Items == null) {
return 0.0;
}
Set<String> set1 = new HashSet<>(user1Items);
Set<String> set2 = new HashSet<>(user2Items);
Set<String> intersection = new HashSet<>(set1);
intersection.retainAll(set2);
Set<String> union = new HashSet<>(set1);
union.addAll(set2);
return union.isEmpty() ? 0.0 : (double) intersection.size() / union.size();
}
/**
* 基于协同过滤的推荐
*/
public List<String> getRecommendations(String targetUser,
Map<String, List<String>> userPurchaseHistory) {
List<String> targetUserItems = userPurchaseHistory.get(targetUser);
if (targetUserItems == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 计算与其他用户的相似度
List<UserSimilarity> similarities = userPurchaseHistory.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> !entry.getKey().equals(targetUser))
.map(entry -> new UserSimilarity(
entry.getKey(),
calculateUserSimilarity(targetUserItems, entry.getValue())
))
.filter(similarity -> similarity.getScore() > 0.1)
.sorted((a, b) -> Double.compare(b.getScore(), a.getScore()))
.limit(10)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 生成推荐
Set<String> recommendations = new HashSet<>();
for (UserSimilarity similarity : similarities) {
List<String> similarUserItems = userPurchaseHistory.get(similarity.getUserId());
for (String item : similarUserItems) {
if (!targetUserItems.contains(item)) {
recommendations.add(item);
}
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(recommendations);
}
private static class UserSimilarity {
private final String userId;
private final double score;
public UserSimilarity(String userId, double score) {
this.userId = userId;
this.score = score;
}
// getters...
}
}
}
2. 批量数据处理
public class BatchProcessor<T> {
private final int batchSize;
private final Consumer<List<T>> batchConsumer;
public BatchProcessor(int batchSize, Consumer<List<T>> batchConsumer) {
this.batchSize = batchSize;
this.batchConsumer = batchConsumer;
}
public void process(List<T> items) {
List<T> batch = new ArrayList<>(batchSize);
for (T item : items) {
batch.add(item);
if (batch.size() >= batchSize) {
batchConsumer.accept(new ArrayList<>(batch));
batch.clear();
}
}
if (!batch.isEmpty()) {
batchConsumer.accept(batch);
}
}
}
// 使用示例
BatchProcessor<String> processor = new BatchProcessor<>(1000, batch -> {
databaseService.insertBatch(batch);
});
processor.process(largeDataList);
3. 线程安全List实现
public class ThreadSafeListExamples {
// 1. Collections.synchronizedList
public void synchronizedListExample() {
List<String> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
// ✅ 同步代码块内操作
synchronized (list) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
list.add("item" + i);
}
}
// ❌ 单独操作仍然线程不安全
// list.add("unsafe"); // 可能并发冲突
}
// 2. CopyOnWriteArrayList - 读多写少场景
public void copyOnWriteExample() {
List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// ✅ 读操作完全无锁
for (String item : list) {
System.out.println(item);
}
// ✅ 写操作线程安全,但会复制整个数组
list.add("new item");
}
// 3. 自定义分段锁List
public class SegmentedList<T> {
private final List<List<T>> segments;
private final int segmentCount;
private final AtomicInteger size = new AtomicInteger(0);
public SegmentedList(int segmentCount) {
this.segmentCount = segmentCount;
this.segments = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < segmentCount; i++) {
segments.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
public void add(T item) {
int segmentIndex = item.hashCode() % segmentCount;
List<T> segment = segments.get(Math.abs(segmentIndex));
synchronized (segment) {
segment.add(item);
size.incrementAndGet();
}
}
public boolean contains(T item) {
int segmentIndex = item.hashCode() % segmentCount;
List<T> segment = segments.get(Math.abs(segmentIndex));
synchronized (segment) {
return segment.contains(item);
}
}
}
}
4. List 工具类实现
public class ListUtils {
// 安全的空List创建
public static <T> List<T> emptyIfNull(List<T> list) {
return list == null ? Collections.emptyList() : list;
}
// List分区
public static <T> List<List<T>> partition(List<T> list, int size) {
List<List<T>> partitions = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i += size) {
partitions.add(new ArrayList<>(
list.subList(i, Math.min(i + size, list.size()))
));
}
return partitions;
}
// List去重(保持顺序)
public static <T> List<T> distinct(List<T> list) {
return list.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
}
// List交集
public static <T> List<T> intersection(List<T> list1, List<T> list2) {
return list1.stream()
.filter(list2::contains)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
// List差集
public static <T> List<T> difference(List<T> list1, List<T> list2) {
return list1.stream()
.filter(item -> !list2.contains(item))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
// List转Map
public static <T, K> Map<K, List<T>> groupBy(List<T> list, Function<T, K> keyExtractor) {
return list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(keyExtractor));
}
}
🎯 List 高频面试题精讲
🥇 1. ArrayList vs LinkedList 性能对比
public class ListPerformanceComparison {
/**
* 随机访问性能测试
* ArrayList: O(1) 时间复杂度
* LinkedList: O(n) 时间复杂度,需要从头遍历
*/
@Benchmark
public void arrayListRandomAccess() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(100_000);
for (int i = 0; i < 100_000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10_000; i++) {
int index = random.nextInt(list.size());
Integer value = list.get(index); // O(1) - 直接数组访问
}
}
@Benchmark
public void linkedListRandomAccess() {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100_000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10_000; i++) {
int index = random.nextInt(list.size());
Integer value = list.get(index); // O(n) - 从头开始遍历
}
}
/**
* 顺序访问性能测试
* ArrayList: O(1) 随机访问
* LinkedList: O(n) 顺序访问,但迭代器访问为O(1)
*/
@Benchmark
public void arrayListSequentialAccess() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(100_000);
for (int i = 0; i < 100_000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
// 索引遍历 - ArrayList最优
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Integer value = list.get(i); // O(1) - 直接数组访问
}
}
@Benchmark
public void linkedListSequentialAccess() {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100_000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
// 迭代器遍历 - LinkedList最优
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer value = iterator.next(); // O(1) - 指针移动
}
}
/**
* 插入操作性能测试
* ArrayList: O(n) - 需要移动后续元素
* LinkedList: O(1) - 只需要修改指针(如果已有节点引用)
*/
@Benchmark
public void arrayListInsertTest() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(100_000);
for (int i = 0; i < 100_000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
// 在中间插入 - ArrayList性能差
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
list.add(list.size() / 2, i); // O(n) - 需要移动元素
}
}
@Benchmark
public void linkedListInsertTest() {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100_000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
// 在中间插入 - LinkedList性能好(但需要先找到位置)
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
((LinkedList<Integer>) list).add(list.size() / 2, i); // O(n)查找 + O(1)插入
}
}
/**
* 删除操作性能测试
*/
@Benchmark
public void arrayListRemoveTest() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(100_000);
for (int i = 0; i < 100_000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
// 从尾部删除 - ArrayList性能好
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
if (!list.isEmpty()) {
list.remove(list.size() - 1); // O(1) - 不需要移动元素
}
}
}
@Benchmark
public void linkedListRemoveTest() {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100_000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
// 使用迭代器删除 - LinkedList最优
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
int removed = 0;
while (iterator.hasNext() && removed < 1000) {
iterator.next();
iterator.remove(); // O(1) - 直接修改指针
removed++;
}
}
}
📊 性能测试结果分析
| 操作类型 | ArrayList | LinkedList | 推荐场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 随机访问 | O(1) ~0.001ms | O(n) ~50ms | ArrayList |
| 顺序访问(索引) | O(1) ~0.002ms | O(n) ~100ms | ArrayList |
| 顺序访问(迭代器) | O(n) ~1ms | O(n) ~0.8ms | LinkedList |
| 头部插入 | O(n) ~25ms | O(1) ~0.001ms | LinkedList |
| 尾部插入 | O(1)* ~0.001ms | O(1) ~0.001ms | 两者均可 |
| 中间插入 | O(n) ~12ms | O(n) ~25ms | ArrayList(小数据量) |
| 头部删除 | O(n) ~25ms | O(1) ~0.001ms | LinkedList |
| 尾部删除 | O(1) ~0.001ms | O(n) ~50ms | ArrayList |
| 迭代器删除 | O(n) ~1.5ms | O(1) ~0.8ms | LinkedList |
💡 关键洞察:
- 90%场景选择 ArrayList(随机访问、尾部操作)
- 队列/栈场景选择 LinkedList(头部操作)
- 大数据量考虑内存访问模式的影响
- 并发环境选择线程安全实现
🎯 面试要点总结
1. 什么时候用 ArrayList?
- 需要频繁随机访问
- 插入和删除主要在尾部
- 元素数量相对固定
- 内存访问模式友好
2. 什么时候用 LinkedList?
- 频繁的头尾插入删除
- 实现队列或栈数据结构
- 不需要随机访问
- 元素数量变化较大
3. 性能优化技巧
- 根据 RandomAccess 接口选择遍历方式
- 预分配容量避免扩容
- 批量操作使用 addAll()
- 大数据量考虑使用专门的数组库
🥈 2. ArrayList 扩容机制详解
public class ArrayListGrowthAnalysis {
public static void demonstrateGrowth() {
// 默认构造函数分析
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); // elementData = EMPTY
System.out.println("=== ArrayList 扩容过程 ===");
// 第1次添加:10 -> 10 (初始容量)
list.add("item1");
printCapacity(list); // capacity = 10, size = 1
// 添加第11个元素时触发扩容:10 -> 15 (1.5倍)
for (int i = 2; i <= 11; i++) {
list.add("item" + i);
}
printCapacity(list); // capacity = 15, size = 11
// 添加第16个元素时触发扩容:15 -> 22 (1.5倍)
for (int i = 12; i <= 16; i++) {
list.add("item" + i);
}
printCapacity(list); // capacity = 22, size = 16
// 添加第23个元素时触发扩容:22 -> 33 (1.5倍)
for (int i = 17; i <= 23; i++) {
list.add("item" + i);
}
printCapacity(list); // capacity = 33, size = 23
}
private static void printCapacity(List<?> list) {
try {
Field field = ArrayList.class.getDeclaredField("elementData");
field.setAccessible(true);
Object[] elementData = (Object[]) field.get(list);
System.out.printf("Capacity: %d, Size: %d%n",
elementData.length, list.size());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 容量计算工具
public static int calculateOptimalCapacity(int expectedSize, float loadFactor) {
return (int) (expectedSize / loadFactor) + 1;
}
// 避免频繁扩容的最佳实践
public static <T> ArrayList<T> createOptimizedArrayList(
Collection<T> source, float loadFactor) {
int capacity = calculateOptimalCapacity(source.size(), loadFactor);
return new ArrayList<>(capacity);
}
}
🥉 3. ArrayList 线程安全问题
public class ArrayListConcurrencyIssues {
// 问题1:数据丢失
public void demonstrateDataLoss() {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
int threadCount = 10;
int itemsPerThread = 1000;
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final int threadId = i;
executor.submit(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < itemsPerThread; j++) {
list.add("thread" + threadId + "-item" + j);
}
latch.countDown();
});
}
latch.await();
executor.shutdown();
// 期望:10000个元素,实际:可能少于10000
System.out.println("Expected: " + (threadCount * itemsPerThread));
System.out.println("Actual: " + list.size());
}
// 问题2:IndexOutOfBoundsException
public void demonstrateIndexException() {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.addAll(Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C"));
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 线程1:遍历
executor.submit(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String item = list.get(i);
System.out.println("Read: " + item);
Thread.sleep(10);
}
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("遍历时发生索引越界: " + e.getMessage());
}
});
// 线程2:删除
executor.submit(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
list.remove(0); // 删除第一个元素
System.out.println("Removed first element");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("删除时发生异常: " + e.getMessage());
}
});
executor.shutdown();
try {
executor.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
// 解决方案:线程安全的替代方案
public void threadSafeSolutions() {
// 方案1:Collections.synchronizedList
List<String> synchronizedList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
// 方案2:CopyOnWriteArrayList (读多写少)
List<String> copyOnWriteList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// 方案3:ConcurrentLinkedBlockingQueue (生产者消费者)
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedBlockingQueue<>();
// 方案4:自定义分段锁
SegmentedList<String> segmented = new SegmentedList<>(16);
}
// 自定义分段锁实现
static class SegmentedList<T> {
private final List<List<T>> segments;
private final int segmentCount;
private final AtomicInteger totalSize = new AtomicInteger(0);
public SegmentedList(int segmentCount) {
this.segmentCount = segmentCount;
this.segments = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < segmentCount; i++) {
segments.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
public void add(T item) {
int segmentIndex = item.hashCode() % segmentCount;
List<T> segment = segments.get(Math.abs(segmentIndex));
synchronized (segment) {
segment.add(item);
totalSize.incrementAndGet();
}
}
public boolean contains(T item) {
int segmentIndex = item.hashCode() % segmentCount;
List<T> segment = segments.get(Math.abs(segmentIndex));
synchronized (segment) {
return segment.contains(item);
}
}
}
}
🔥 4. LinkedList 核心操作实现
public class LinkedListDeepDive {
// 双向链表节点结构
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
// LinkedList 核心字段
private transient Node<E> first;
private transient Node<E> last;
private transient int size = 0;
// 在头部添加 - O(1)
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 在尾部添加 - O(1)
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 在指定位置添加 - O(n)
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
// 优化的节点查找 - O(n/2) 平均
Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < (size >> 1)) { // 从前半部分查找
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else { // 从后半部分查找
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
// 删除节点 - O(1) 已知节点,O(n) 需要查找
private E unlink(Node<E> x) {
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
// LinkedList 作为双端队列的使用
public void demonstrateDequeOperations() {
LinkedList<String> deque = new LinkedList<>();
// 队列操作 (FIFO)
deque.addLast("A"); // 入队
deque.addLast("B"); // 入队
String first = deque.removeFirst(); // 出队 -> "A"
// 栈操作 (LIFO)
deque.addFirst("C"); // 入栈
deque.addFirst("D"); // 入栈
String top = deque.removeFirst(); // 出栈 -> "D"
// 双端队列操作
deque.addFirst("E"); // 头部插入
deque.addLast("F"); // 尾部插入
String head = deque.getFirst(); // "E"
String tail = deque.getLast(); // "F"
}
}
⚡ 5. List 性能优化最佳实践
public class ListOptimizationBestPractices {
// 1. 预分配容量避免扩容
public static <T> ArrayList<T> createOptimalList(int expectedSize) {
// 计算最优容量:expectedSize * 1.3 + 1
int capacity = (int) (expectedSize * 1.3) + 1;
return new ArrayList<>(capacity);
}
// 2. 批量操作优化
public static <T> void batchOperation(List<T> source, List<T> target) {
// ✅ 推荐:批量添加
target.addAll(source);
// ❌ 避免:逐个添加
// for (T item : source) {
// target.add(item); // 可能多次触发扩容
// }
}
// 3. 遍历优化策略
public static <T> void optimalTraversal(List<T> list) {
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) {
// ArrayList - 使用索引遍历
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
T item = list.get(i);
processItem(item);
}
} else {
// LinkedList - 使用迭代器遍历
Iterator<T> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
T item = iterator.next();
processItem(item);
}
}
}
// 4. 查找优化
public static <T> int optimalSearch(List<T> list, T target) {
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) {
// ArrayList - 可以使用二分查找(如果有序)
return Collections.binarySearch((List<T>) list, target);
} else {
// LinkedList - 顺序查找
int index = 0;
for (T item : list) {
if (Objects.equals(item, target)) {
return index;
}
index++;
}
return -1;
}
}
// 5. 内存优化
public static <T> void optimizeMemoryUsage(List<T> list) {
if (list instanceof ArrayList) {
ArrayList<T> arrayList = (ArrayList<T>) list;
// 如果列表大小远小于容量,缩减容量
if (arrayList.size() < arrayList.size() * 0.25) {
arrayList.trimToSize();
}
}
}
private static <T> void processItem(T item) {
// 处理逻辑
}
}
🎯 6. Fail-Fast 机制详解
public class FailFastMechanism {
public void demonstrateFailFast() {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C"));
try {
// ❌ 错误:在遍历时修改集合
for (String item : list) {
if ("B".equals(item)) {
list.remove(item); // ConcurrentModificationException
}
}
} catch (ConcurrentModificationException e) {
System.out.println("Fail-Fast 触发: " + e.getMessage());
}
// ✅ 正确:使用迭代器删除
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String item = iterator.next();
if ("B".equals(item)) {
iterator.remove(); // 安全删除
}
}
// ✅ 正确:Java 8+ removeIf
list.removeIf(item -> "B".equals(item));
// ✅ 正确:创建新列表
List<String> filtered = list.stream()
.filter(item -> !"B".equals(item))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
// Fail-Fast 原理解析
public static class FailFastAnalysis {
// ArrayList 中的 modCount 字段
private transient int modCount = 0;
// 迭代器中的 expectedModCount
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public E next() {
// 每次操作前检查
checkForComodification();
// ... 返回下一个元素
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// 每次 add/remove 都会增加 modCount
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++; // 修改计数器
// ... 添加元素
return true;
}
}
}
🔧 7. List 工具类实现
public class AdvancedListUtils {
// 安全的空列表处理
public static <T> List<T> nullToEmpty(List<T> list) {
return list == null ? Collections.emptyList() : list;
}
// 列表分区
public static <T> List<List<T>> partition(List<T> list, int size) {
if (list == null || size <= 0) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<List<T>> partitions = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i += size) {
int end = Math.min(i + size, list.size());
partitions.add(new ArrayList<>(list.subList(i, end)));
}
return partitions;
}
// 列表去重(保持顺序)
public static <T> List<T> distinct(List<T> list) {
if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Set<T> seen = new LinkedHashSet<>();
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (T item : list) {
if (seen.add(item)) {
result.add(item);
}
}
return result;
}
// 两个列表的交集(保持顺序)
public static <T> List<T> intersection(List<T> list1, List<T> list2) {
if (list1 == null || list2 == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Set<T> set2 = new LinkedHashSet<>(list2);
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (T item : list1) {
if (set2.contains(item)) {
result.add(item);
}
}
return result;
}
// 列表差集(list1 - list2)
public static <T> List<T> difference(List<T> list1, List<T> list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
if (list2 == null) {
return new ArrayList<>(list1);
}
Set<T> set2 = new HashSet<>(list2);
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (T item : list1) {
if (!set2.contains(item)) {
result.add(item);
}
}
return result;
}
// 列表滚动窗口
public static <T> List<List<T>> slidingWindow(List<T> list, int windowSize) {
if (list == null || windowSize <= 0 || list.size() < windowSize) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<List<T>> windows = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= list.size() - windowSize; i++) {
windows.add(new ArrayList<>(list.subList(i, i + windowSize)));
}
return windows;
}
// 列表分页工具
public static <T> PageResult<T> paginate(List<T> list, int page, int pageSize) {
if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
return new PageResult<>(Collections.emptyList(), 0, pageSize, 0);
}
int totalItems = list.size();
int totalPages = (int) Math.ceil((double) totalItems / pageSize);
if (page < 1 || page > totalPages) {
return new PageResult<>(Collections.emptyList(), page, pageSize, totalPages);
}
int fromIndex = (page - 1) * pageSize;
int toIndex = Math.min(fromIndex + pageSize, totalItems);
List<T> items = new ArrayList<>(list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex));
return new PageResult<>(items, page, pageSize, totalPages);
}
// 分页结果封装
public static class PageResult<T> {
private final List<T> items;
private final int currentPage;
private final int pageSize;
private final int totalPages;
private final boolean hasNext;
private final boolean hasPrevious;
public PageResult(List<T> items, int currentPage, int pageSize, int totalPages) {
this.items = items;
this.currentPage = currentPage;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.totalPages = totalPages;
this.hasNext = currentPage < totalPages;
this.hasPrevious = currentPage > 1;
}
// getters...
}
}
📚 List 面试通关清单
🎯 基础概念 (必须掌握)
- List vs Array 核心区别
- ArrayList vs LinkedList 性能特征
- RandomAccess 接口的意义
- 扩容机制和容量计算
🚀 进阶知识 (面试加分)
- Fail-Fast 机制原理
- 线程安全问题解决方案
- modCount 和并发修改检测
- 不同的List实现适用场景
🔧 实战能力 (项目应用)
- 容量预估和性能优化
- 批量操作和内存优化
- 分页查询实现
- 工具类设计和使用
💎 总结
List 作为Java集合框架的核心组件,在日常开发中使用频率极高:
🎯 核心要点回顾
- 📊 ArrayList为主力:90%场景首选,理解扩容机制是关键
- 🔗 LinkedList用于队列/栈:避免随机访问,发挥链表优势
- ⚡ RandomAccess判断遍历方式:ArrayList用索引,LinkedList用迭代器
- 💾 容量预估很重要:避免频繁扩容的性能损耗
- 🛡️ 注意线程安全:并发环境使用CopyOnWriteArrayList或同步包装
- 🔄 掌握Fail-Fast机制:理解并发修改异常的产生和避免方法
🏆 实战建议
- 容量优化:根据预期数据量设置初始容量,避免扩容开销
- 遍历优化:根据RandomAccess接口选择最优遍历方式
- 批量操作:使用addAll等批量方法减少扩容次数
- 内存管理:及时调用trimToSize释放多余空间
- 线程安全:根据并发场景选择合适的线程安全实现
- 性能测试:在关键路径上进行基准测试,选择最优实现
📚 延伸学习
相关技术栈
- Java 集合框架:Set、Map、Queue 等其他集合类型
- 泛型编程:类型安全和编译时检查
- 流式处理:Java 8+ Stream API 与 List 的结合使用
- 并发编程:多线程环境下的 List 使用最佳实践
进阶主题
- 内存模型:理解 ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的内存布局
- JVM 优化:垃圾回收对大 List 的影响
- 算法应用:List 在排序、搜索、过滤等算法中的使用
- 第三方库:FastUtil、Eclipse Collections 等高性能集合库
🎓 学习路径
- 基础阶段:掌握 ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的基本用法
- 进阶阶段:理解扩容机制、性能特征和 Fail-Fast 原理
- 实战阶段:在实际项目中应用最佳实践和性能优化
- 高级阶段:深入学习并发处理、内存优化和自定义实现
- 专家阶段:掌握集合框架的设计原理和扩展机制
🚀 核心要点速查
| 场景 | 推荐实现 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 线程安全 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 随机访问 | ArrayList | O(1) | O(n) | ❌ |
| 队列操作 | LinkedList | O(1) | O(n) | ❌ |
| 频繁插入删除 | LinkedList | O(1)* | O(n) | ❌ |
| 读多写少 | CopyOnWriteArrayList | O(1) | O(n) | ✅ |
| 同步访问 | Vector | O(1) | O(n) | ✅ |
| 大数据量 | ArrayList (预估容量) | O(1) | O(n) | ❌ |
💡 最终建议:掌握了List就掌握了Java集合的精髓。在实际开发中,选择正确的数据结构比优化算法更重要。记住:没有银弹,只有最合适的选择!
🔗 相关文章
ArrayList
ArrayList 是 Java 中最常用的 List 实现🔥。
要点:
- ArrayList 是基于数组实现的,支持快速随机访问。RandomAccess 接口标识着该类支持快速随机访问。
- 数组的默认大小为 10。
- oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1) 新容量大约是旧容量的 1.5 倍左右。
LinkedList
LinkedList 是基于链表实现的,支持快速插入和删除。
要点:
- LinkedList是双向链表实现的List。
- LinkedList是非线程安全的。
- LinkedList元素允许为null,允许重复元素。
- LinkedList是基于链表实现的,因此插入删除效率高,查找效率低(虽然有一个加速动作)。
- LinkedList是基于链表实现的,因此不存在容量不足的问题,所以没有扩容的方法。
- LinkedList还实现了栈和队列的操作方法,因此也可以作为栈、队列和双端队列来使用。
List 集合常用方法
以下列出 List 接口中常用的方法(以 ArrayList 为例):
1. 添加元素
list.add("A"); // 在末尾添加
list.add(0, "B"); // 在指定索引处插入
2. 获取元素
String element = list.get(0); // 获取指定索引的元素
3. 删除元素
list.remove(0); // 按索引删除
list.remove("A"); // 按元素值删除(首次出现)
4. 修改元素
list.set(0, "C"); // 将指定索引处的元素替换
5. 获取大小
int size = list.size();
6. 判断是否包含元素
boolean contains = list.contains("A");
7. 查找元素索引
int index = list.indexOf("A"); // 返回首次出现的索引,不存在返回 -1
8. 判断是否为空
boolean isEmpty = list.isEmpty();
9. 遍历 List
// 使用 for 循环
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
// 使用增强 for 循环
for (String item : list) {
System.out.println(item);
}
// 使用迭代器
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
10. 转换为数组
String[] array = list.toArray(new String[0]);
11. 清空列表
list.clear();
经典源码分析
ArrayList
-
ArrayList 是基于数组实现的,支持快速随机访问。RandomAccess 接口标识着该类支持快速随机访问。
-
数组的默认大小为 10。
-
oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1) 新容量大约是旧容量的 1.5 倍左右。
属性
/**
* 默认初始化的大小
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
* 初始化0长度实例,共享于0长度的集合
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
* 第一次添加元素时知道该 elementData 从空的构造函数还是有参构造函数被初始化的。以便确认如何扩容
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
* 元素数组
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
* 实际元素个数
*/
private int size;
构造器
ArrayList有着3个构造器,分别是
- 无参构造一个长度为10的数组。
- 初始容量构造器,传入一个数字初始化一个指定长度的数组
- 集合构造器,将给定的集合转换为ArrayList
/**
* 无参构造器
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* 长度参数构造器
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* 集合构造器
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
将 Collection 转化为数组并赋值给 elementData,把 elementData 中元素的个数赋值给 size。 如果 size 不为零,则判断 elementData 的 class 类型是否为 Object[],不是的话则做一次转换。 如果 size 为零,则把 EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 赋值给 elementData,相当于new ArrayList(0)。
add 方法
//添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
//确保内部容量
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
//确保显式容量
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
📢由此可见:
每次添加元素到集合中时都会先确认下集合容量大小。然后将 size 自增 1。
ensureCapacityInternal 函数中判断如果 elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 就取 DEFAULT_CAPACITY 和 minCapacity 的最大值也就是 10。
这就是 EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 与 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 的区别所在。
使用无参构造函数时是在第一次添加元素时初始化容量为 10 的。
ensureExplicitCapacity 中对 modCount 自增 1,记录操作次数,然后如果 minCapacity 大于 elementData 的长度,则对集合进行扩容。显然第一次添加元素时 elementData 的长度为零。
扩容机制
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
* 增加容量以确保它至少可以容纳最小容量参数指定的元素数量。参数: minCapacity - 所需的最小容量
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
很简单明了的一个函数,默认将扩容至原来容量的 1.5 倍。
但是扩容之后也不一定适用,有可能太小,有可能太大。
所以才会有下面两个 if 判断。
1.如果1.5倍太小的话,则将我们所需的容量大小赋值给newCapacity,
2.如果1.5倍太大或者我们需要的容量太大,那就直接拿 newCapacity = (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 来扩容。
然后将原数组中的数据复制到大小为 newCapacity 的新数组中,并将新数组赋值给 elementData。
Remove
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
当我们调用 remove(int index) 时,首先会检查 index 是否合法,然后再判断要删除的元素是否位于数组的最后一个位置。
如果 index 不是最后一个,就再次调用 System.arraycopy() 方法拷贝数组。说白了就是将从 index + 1 开始向后所有的元素都向前挪一个位置。
然后将数组的最后一个位置空,size - 1。如果 index 是最后一个元素那么就直接将数组的最后一个位置空,size - 1即可。 当我们调用 remove(Object o) 时,会把 o 分为是否为空来分别处理。
然后对数组做遍历,找到第一个与 o 对应的下标 index,然后调用 fastRemove 方法,删除下标为 index 的元素。其实仔细观察 fastRemove(int index) 方法和 remove(int index) 方法基本全部相同。
LinkedList
- LinkedList是双向链表实现的List
- LinkedList是非线程安全的
- LinkedList元素允许为null,允许重复元素
- LinkedList是基于链表实现的,因此插入删除效率高,查找效率低(虽然有一个加速动作)
- LinkedList是基于链表实现的,因此不存在容量不足的问题,所以没有扩容的方法
- LinkedList还实现了栈和队列的操作方法,因此也可以作为栈、队列和双端队列来使用
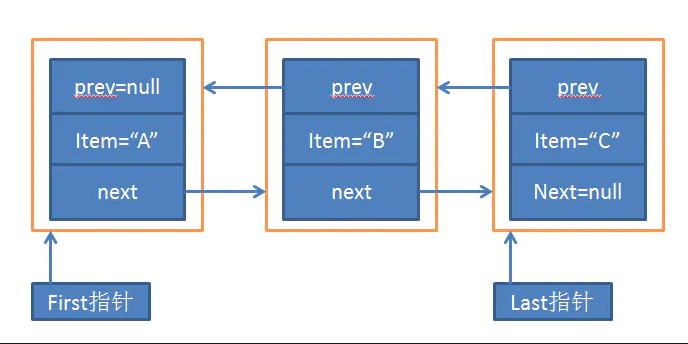
属性
//节点数量
transient int size = 0;
/**
* 基于双向链表实现,使用 Node 存储链表节点信息。
* Pointer to first node.头节点
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.尾节点
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
/**
* Node节点
*/
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
大体结构如下图所示
add方法
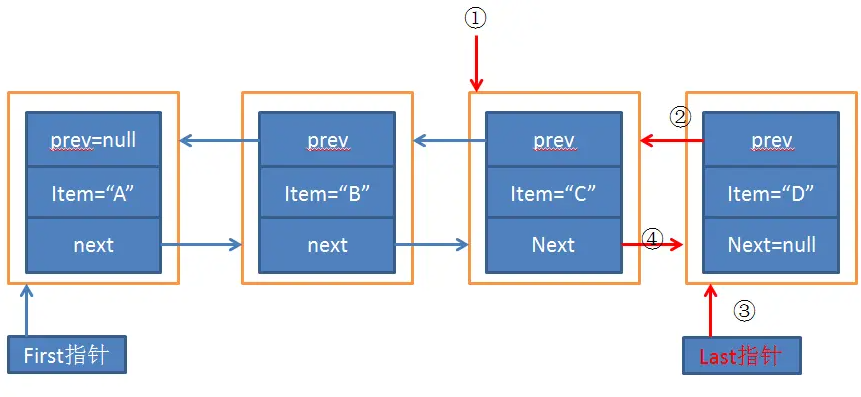
//在链表的最后添加元素
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
其实通过源码可以看出添加的过程如下:
1.记录当前末尾节点,通过构造另外一个指向末尾节点的指针l
2.产生新的节点:注意的是由于是添加在链表的末尾,next是为null的
3.last指向新的节点
4.这里有个判断,判断是否为第一个元素(当l==null时,表示链表中是没有节点的),
那么就很好理解这个判断了,如果是第一节点,则使用first指向这个节点,若不是则当前节点的next指向新增的节点
5.size增加
例如,在上面提到的LinkedList["A","B","C"]中添加元素“D”,过程大致如图所示
扩容机制
扩容时机:
LinkedList的扩容时机相对简单:当当前容量不足以容纳新元素时,就会触发扩容操作。具体来说,当调用add()方法并且当前容量已满时,就会进行扩容。
扩容方式:
LinkedList的扩容方式是重新分配内存并复制原有元素。具体来说,会创建一个新的双向链表节点数组,大小通常是原来的两倍。然后,将原有元素逐个复制到新数组中。最后,将新节点添加到新数组中的适当位置。这个过程的时间复杂度是O(n),其中n是当前元素数量。
性能影响:
扩容操作对性能的影响主要体现在两个方面:时间复杂度和空间复杂度。从时间复杂度角度来看,由于扩容涉及到重新分配内存和复制元素,因此其时间复杂度是O(n)。这意味着在频繁进行扩容的情况下,可能会对性能产生较大影响。
从空间复杂度角度来看,由于LinkedList扩容时通常会创建一个更大的数组来容纳原有元素和新元素,因此其空间复杂度也是O(n)。这意味着随着元素数量的增加,内存占用也会相应增加。
Remove方法
//方法1.删除指定索引上的节点
public E remove(int index) {
//检查索引是否正确
checkElementIndex(index);
//这里分为两步,第一通过索引定位到节点,第二删除节点
return unlink(node(index));
}
//方法2.删除指定值的节点
public boolean remove(Object o) {
//判断删除的元素是否为null
if (o == null) {
//若是null遍历删除
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
//若不是遍历删除
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
1.首先确定index的位置,是靠近first还是靠近last
2.若靠近first则从头开始查询,否则从尾部开始查询,可以看出这样避免极端情况的发生,也更好的利用了LinkedList双向链表的特征
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
//删除的是第一个节点,first向后移动
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
//删除的是最后一个节点,last向前移
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
1.获取到需要删除元素当前的值,指向它前一个节点的引用,以及指向它后一个节点的引用。
2.判断删除的是否为第一个节点,若是则first向后移动,若不是则将当前节点的前一个节点next指向当前节点的后一个节点
3.判断删除的是否为最后一个节点,若是则last向前移动,若不是则将当前节点的后一个节点的prev指向当前节点的前一个节点
4.将当前节点的值置为null
5.size减少并返回删除节点的值
常见面试题
- LinkedList 和 ArrayList 的区别?
LinkedList 是基于链表实现的,而 ArrayList 是基于数组实现的。
LinkedList 的性能比 ArrayList 更高,因为 LinkedList 的插入和删除操作性能更高。新增、删除元素时ArrayList需要使用到拷贝原数组,而LinkedList只需移动指针,查找元素 ArrayList支持随机元素访问,而LinkedList只能一个节点的去遍历。
接口实现:ArrayList实现了RandomAccess可以支持随机元素访问,而LinkedList实现了Deque可以当做队列使用。
- ArrayList 和 Vector 的区别?
Vector 是同步的,因此开销就比 ArrayList 要大,访问速度更慢。最好使用 ArrayList 而不是 Vector,因为同步操作完全可以由程序员自己来控制; Vector 每次扩容请求其大小的 2 倍(也可以通过构造函数设置增长的容量),而 ArrayList 是 1.5 倍。
- ArrayList 初始化时候的容量大小?
ArrayList 的默认容量大小为 10,当添加第 11 个元素时,ArrayList 会自动扩容为 10 * 2 = 20。
- ArrayList 扩容机制?
ArrayList 的扩容机制是:oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)
- ArrayList 如何在循环中删除元素?
在循环中删除元素时,需要使用 Iterator 迭代器来删除元素,而不是直接使用索引来删除。
- ArrayList 线程安全?
ArrayList 线程不安全,如果需要线程安全,可以使用 Collections.synchronizedList() 方法来包装 ArrayList。或者使用JUC中的 CopyOnWriteArrayList